Accumulation of Fat in the Liver
It is literally a disease caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Particularly, triglycerides accumulate in hepatocytes, causing the liver to fail to function properly. The liver is a called chemical factory of the human body and a detoxification factory, and it plays various roles. Fatty liver occurs when the fat ingested through food cannot be processed properly.
Fatty liver is the most common liver disease in Western society. About 20-30% of Americans get sick with this. However, there are not many subjective symptoms, so there are many cases that the person does not know. It tends to occur more in women than in men. It usually occurs after the age of 50, but it can happen at any time.
There are 2 kinds of fatty livers.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). It is fatty liver, but there is no inflammation in the liver.
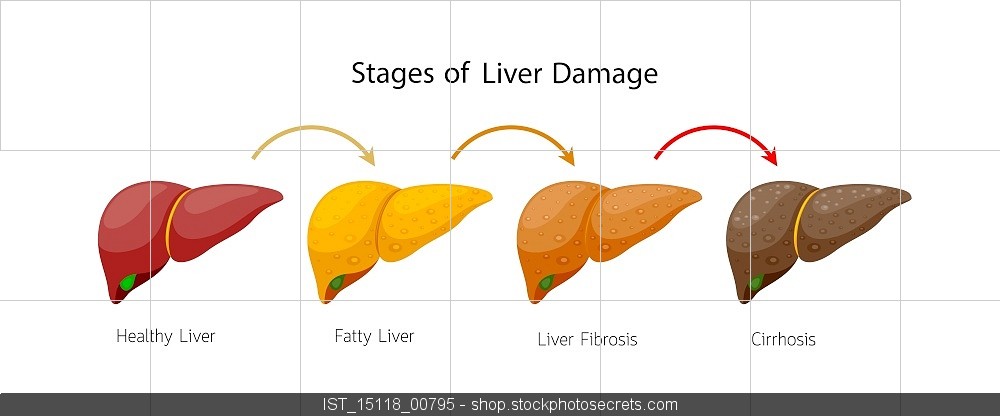
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). It is fatty liver with inflammation in the liver. This may progress to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are the risk factors?
Obesity. Diabetes. Hyperlipidemia, especially when triglycerides are high. Sudden weight loss.
What are the symptoms?
In most cases, there are no symptoms, and diagnosis is difficult with symptoms alone. Common symptoms of liver disease include chronic fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, discomfort or slight pain in the right upper abdomen.
How do we make the diagnosis?
When liver function tests through blood tests are performed, AST and ALT, which represent liver enzymes levels, increase 2-3 times compared to normal, and drinkers also increase GGT. When the liver level rises, continuous observation is necessary through serial test. In some cases, it is necessary to perform abdominal ultrasound to confirm fatty liver and to check for other liver lesions.
What is prognosis?
Fatty liver depends on its cause, but in most cases, it does not cause major problems.
However, if you continue to drink alcohol, or if obesity, hyperlipidemia, etc. do not improve, you should be careful as it can rarely progress to fatty hepatitis, liver fibrosis, and even liver cirrhosis. If a patient with fatty liver continues to drink more than 14oz of alcohol a week, it is known that about 2% of them develop cirrhosis per year.
Treatment
Treatment of the cause is the most important.
If you drink alcohol often: You should exercise consistently with abstaining from alcohol, at least 30 minutes a day, at least 3 times a week.
If you have obesity or hyperlipidemia: You should keep weight control, reduce high-calorie foods, and eat a lot of fresh fruits and vegetables. In the case of hyperlipidemia, drug therapy is sometimes used.
If you have diabetes: You should control your blood sugar well to lower your hemoglobin A1C. Appropriate diet and exercise are necessary, and in some cases, medications must be combined.
How do you prevent?
Take regular blood tests to diagnose early.
Maintain an appropriate weight steadily, not temporarily.
Avoid heavy drinking, and exercise at least 3 times a week for 30 minutes or more.
Reduce excess carbohydrates and fat intake and eat fresh fruits and vegetables.
Steven Koh, MD
Family Medicine
Edmonds Medical Clinic