Do you have abdominal pain like appendicitis?
Diverticulitis
What is Diverticulitis?
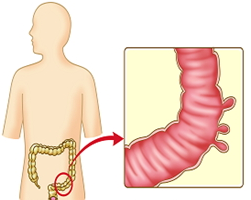
The inner layers of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine weaken, and the inner layers stretches, resulting in a balloon-shaped pouch, which is called the diverticulum. In other words, diverticulum refers to a convex pocket that extends outside the intestine, and structurally, you can think of it as the opposite of ‘polyp’.
What is the difference between diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
- Diverticulum: When there is a single pouch, it is just called ‘diverticulum.’
- Diverticulosis: When there are two or more diverticulum, it is called ‘diverticulosis’, and there are usually no special symptoms
- Diverticulitis: When stool or food debris gets stuck in the diverticulum and causes inflammation / infection / pus, it is called diverticulitis.
What is the cause?
As you get older, the elasticity of the large intestine decreases, and as the pressure in the large intestine increases due to constipation or incorrect eating habits. The inner layer of your intestine pushes through weak spots in the outer lining. The pressure makes them bulge out, making little pouches, and diverticulum occurs.
Prevalence of diverticulum?
– Age over 40: 10%
– Age over 60: 50%
– Age over 80: 70%
Where the diverticulum occurs?
Western societies: It mainly occurs in the left large intestine, especially in the Sigmoid Colon.
Asian: It usually occurs in the right large intestine. However, due to recent westernized dietary changes, the incidence of left colon diverticulum is increasing.
Symptoms?
1. Diverticulosis:
- In most cases there are no symptoms.
- Sometimes, abdominal bloating, mild abdominal pain, and constipation may appear.
2. Diverticulitis:
- This means inflammation or infection of the diverticulum. About 5% of people with diverticulosis may develop diverticulitis.
- Complains of severe abdominal pain, chills, and fever, and the symptoms worsen depending on the degree of inflammation / infection.
- After eating, symptoms worsen. Symptoms will be better after bowel movements.
- The small blood vessels in the diverticulum are repeatedly inflamed and damaged, causing bleeding. Most diverticulum bleeding stops naturally, but when bleeding in large quantities, emergent surgery may be required.
Diagnosis?
Diverticulosis: It can be done with a gastroscopy or colonoscopy and is often found accidentally during regular checkups.
Diverticulitis: It is diagnosed through CT of the abdomen.
Treatment?
- If there are no symptoms initially, no special treatment is required. However, if it develops into diverticulitis and the symptoms worsen, medical treatment is first required.
- Diverticulosis: You need to take a lot of fiber and water. It is necessary to reduce the pressure in the colon by preventing constipation.
- Diverticulitis: Infection and inflammation should be treated by taking antibiotics. You need fasting as much as possible to rest your intestines. Recurrence occurs in 30% of cases.
- Surgery: If medical treatment is ineffective, diverticulitis recurs frequently, peritonitis, or massive bleeding, etc., a selective bowel resection is sometimes required.
Prevention?
- Eat foods with high fiber.
- Drink a lot of water.
- Exercise regularly and maintain an appropriate weight.
- Do not smoke.
Yoon Park, MD (박윤진)
Family Medicine
Edmonds Medical Clinic