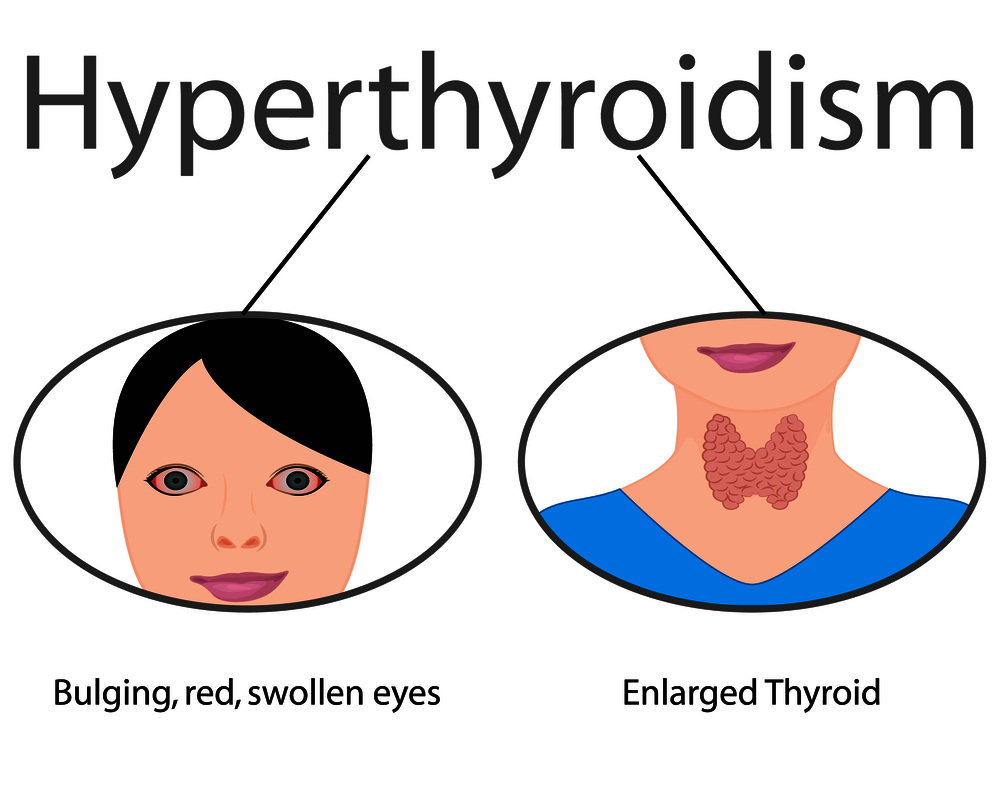
Are you tired easily, sweat a lot, your chest is pounding, and you have a hard time withstand the heat? Hyperthyroidism is suspected.
What is Thyroid Gland?
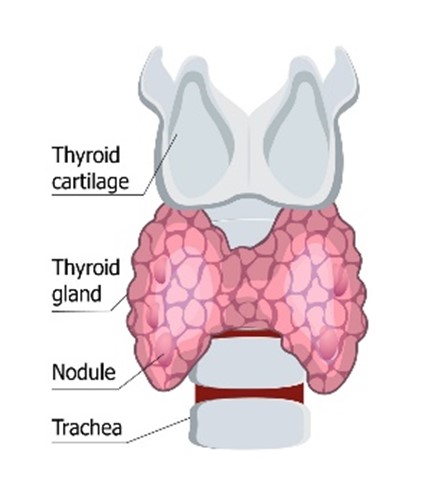
The thyroid gland is an endocrine organ located in the front part of the neck and is responsible for making thyroid hormones. In the middle of the neck, just below the thyroid cartilage that protrudes forward, it is an organ surrounded by a butterfly shape. It is about 2cm wide and 5cm high, and in the case of a normal person, it is not visible and cannot be touched.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
It is a clinical syndrome in which the physiological function of thyroid function is excessive due to an increase in thyroid hormone.
Causes?
- Grave’s disease: The most common case, accounts for 60-80% of hyperthyroidism, and most often occurs between the ages of 20-50. Women have a higher incidence than men. Family history is common as an autoimmune disease.
- Toxic Multinodular Goiter: When there are multiple nodules in the thyroid gland and excessive thyroid hormone secretion.
- Toxic Thyroid Adenoma: 1 benign nodule that secretes excessive thyroid hormone.
- Thyroiditis: This is a temporary hyperactivity caused by inflammation that occurs after childbirth or after a viral or bacterial infection.
Symptoms?
- Weight loss even with good appetite.
- Physical consumption is severe and fatigue is easy.
- Hands and feet shake frequently.
- The heat is generated more, making it difficult to bear the heat.
- Sweat a lot, palpitation, hypertension.
- Increased anxiety and irritability.
- Diarrhea often.
- In the case of women, it may cause menstrual irregularities and infertility.
- Ocular protrusion may occur.
Diagnosis?
- It can be diagnosed through a simple blood test (TSH, T3, T4, thyroid antibody).
- Thyroid ultrasound
Treatment?
- Antithyroid Medications: Medications improves symptoms by interfering with the production of thyroid hormone
- Radioactive Iodine (I-131): Radioactive iodine is administered orally to selectively remove thyroid tissue.
- Surgery: When the thyroid gland is very enlarged and there are pressure symptoms, or when antithyroid medication is not possible, thyroidectomy is performed.
Prognosis/Complication?
If people with hyperthyroidism do not receive adequate treatment, and sudden stress or infection happen, they can lead to thyrotoxicosis. This can be accompanied by high fever, sweating, increased pulse rate, excitement, and loss of consciousness. In addition, complications such as arrhythmia and osteoporosis may occur.
FAQ:
Can I get hypothyroidism if I have a thyroidectomy?
- If the entire thyroid gland is excised: It is essential to take thyroid hormones for life to prevent hypothyroidism.
- If only part of the thyroid gland is resected: If hormone secretion is adequate from the remaining thyroid gland, hormone supplementation is not necessary. However, it is important to perform thyroid function tests regularly and follow up.
Yoon Park, MD
Family Medicine
Edmonds Medical Clinic