GERD (GastroEsophageal Reflux Disease)

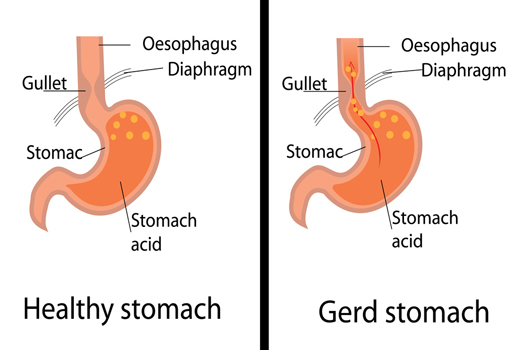
What is GERD?
- There are two gates in the stomach: the cardia from the esophagus to the stomach and the pylorus from the stomach to the duodenum. Among them, the esophageal sphincter is present in the cardia, preventing the contents of the stomach to reaching the esophagus reversely.
- Under normal conditions, the esophageal sphincter opens only when swallowing and belching.
- If the tightening force of the esophageal sphincter is weak or improperly opened, gastric juice will flow back into the esophagus. This reverse flow of stomach acid into the esophagus causes uncomfortable symptoms or complications caused by irritation of stomach acid.
What are the symptoms?
- Frequent acidic belching
- Symptoms of acid regurgitation into the throat or mouth worsen. (The symptoms worsen when you lie down or lean forward.)
- A burning sensation or pain often occurs in the chest area.
- There may be symptoms such as dry cough, frequent hoarseness, and sore throat.
What are the risk factors?
- Pregnant women, smokers, and diabetics tend to have weakened esophageal sphincter, which is more likely to develop this disease.
- If you take drugs such as benzodiazepine or calcium channel blocker, you may develop a disease.
What are the possible complications?
- Barrett’s Esophagus: A disease in which normal squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus become columnar epithelial cells. It is known to cause esophageal cancer. (In other words, it is a disease that is somewhere between normal esophageal cells and esophageal cancer.)
- Chronic cough, chronic sore throat, hoarseness, and asthma may occur.
How is the diagnosis?
- Most diagnoses can be made through a questionnaires and physical exam.
- It can be confirmed by endoscopy and biopsy.
How to treat?
- Gastric acid is the cause of complications of acid reflux, so it can be treated with medications that suppress the secretion of gastric acid.
How to prevent?
- Avoid the following foods: Alcohol, coffee, soda, energy drinks, fatty foods, chocolate, mustards, spicy foods, and foods containing tomatoes like ketchup, pizza, and spaghetti.
Avoid the following medications: Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Advil, Naproxen, Motrin, Aleve. - Avoid overeating.
- You must quit smoking. (Smoking weakens the esophageal sphincter.)
- After eating, stomach acid is easily refluxed, so do not lie down immediately after eating.
- In case of severe esophagitis, it is also helpful to use a high pillow at bedtime.
*The Unsolved Mystery:
How did “7up soft drink” get its name?
- The 1st theory: It contains 7 secret ingredients, and it is said that carbonated bubbles rise up well.
- The 2nd theory: At the time, Coca-Cola was sold in a 6-ounce bottle, but the 7up was sold in a 7-ounce bottle.
- The 3rd theory: After drinking 7up, there is a lot of carbonate, so you may burp at least 7 times.
* It does not matter which theory is correct, but what is certain is that GERD often recurs if you drink a lot of these carbonated soda.
Steven Koh, MD
Family Medicine
Edmonds Medical Clinic