Are you suffering 3 P’s?
November 14th is World Diabetes Day. Let us look at diabetes, which occurs every 10 seconds, 3 patients worldwide.
DM (Diabetes Mellitus)
Symptoms?
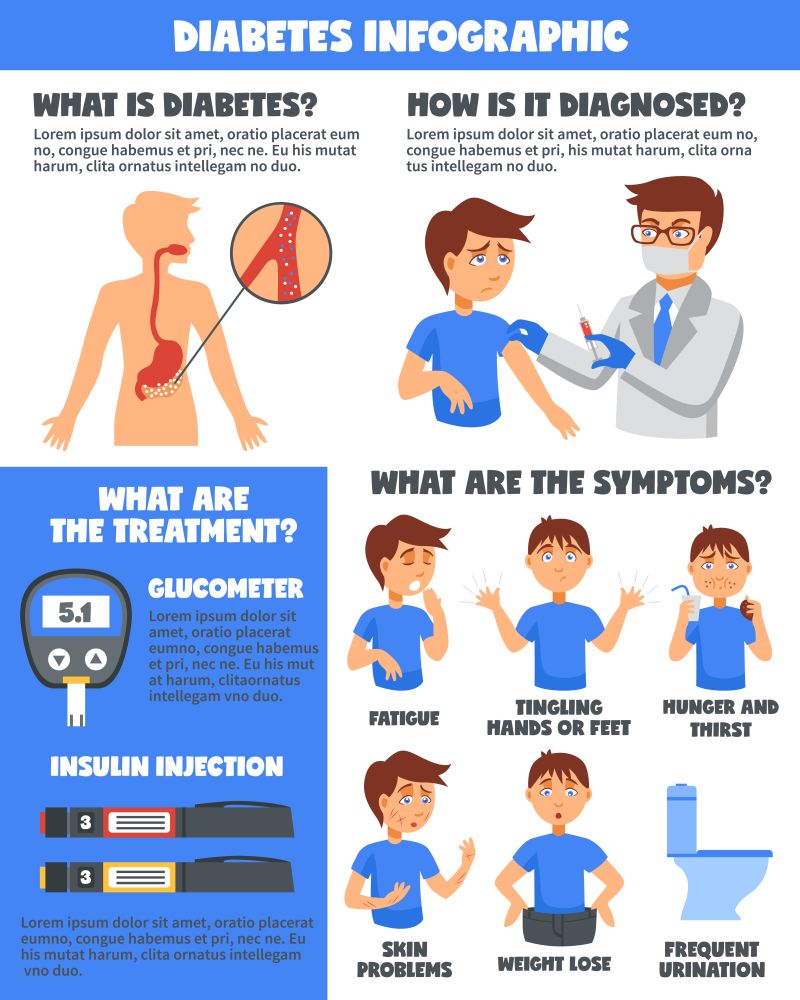
- There are no symptoms at all in the early stages of diabetes, so it is easy to miss it.
- The main symptoms are 3 major symptoms called 3 P’s, which includes ‘Polyuria’ with frequent urination, ‘Polydipsia’ drinking a lot of water, and ‘Polyphagia’ with increased appetite.
- When the blood sugar rises above a certain level, it goes out into the urine. At this time, the amount of urine naturally increases as water goes out. When you lose water, you feel thirst, drink a lot of water, food is not used for energy and drains into the urine, hunger increases, and appetite increases.
- Other symptoms may include faintness in the eyes, numbness in the hands and feet, and vaginal pruritus in women.
- Diabetes is common in obese people, but as the disease progresses, nutrients are lost without being used from the body, making them feel tired and eventually losing weight.
Causes?
- Main causes: obesity, excessive food intake, decreased exercise
- Other causes: heredity, stress, pregnancy, infection, drugs (steroids, immunosuppressants)
- Eating a lot of sweets does not result in diabetes but eating a lot of sweets can result in weight gain, and if you develop obesity, your risk of developing diabetes increases.
Diagnosis?
- If the measured blood sugar is 200mg/dL or higher, regardless of the mealtime.
- If the measured fasting blood sugar is 126mg/dL or higher in an 8-hour fasting state.
- When the blood sugar measured 2 hours after ingesting 75mg of glucose in the oral glucose tolerance test is 200mg/dL or higher.
- If the level is 6.5% or higher in the hemoglobin A1C test.
Types?
- Type 1 diabetes: This is when the pancreas does not secrete insulin properly. There are many pediatric patients, and insulin injections must be used.
- Type 2 diabetes: Insulin is secreted properly, but due to various causes, insulin is not functioning properly. The main cause is obesity. You must take a hypoglycemic drug or use an insulin injection.
Treatments?
- Dietary therapy: You should eat a low-carb diet. Avoid sweet and high-calorie foods.
- Exercise therapy: To reduce fat and strengthen muscles, you must exercise consistently. (It is better to combine aerobic exercise and strength exercise.)
- Pharmacologic therapy: You can start with oral hypoglycemic drugs. If it is not well controlled, you should take non-insulin injection or insulin injection.
Prognosis/Complications?
- Causes chronic inflammation, changes in large and small blood vessels, which are caused by narrowing or blockage.
- Complications of large blood vessels: heart attack, and stroke. (In addition to blood sugar control, it is important to control blood pressure and cholesterol)
- Complications of small blood vessels: visual loss due to diabetic retinopathy, chronic renal failure, decreased sensation and pain in upper and lower extremities, and diabetic foot. (Only thorough blood sugar control can prevent or prevent progression.)
Preventions?
- Things to avoid: obesity, sedentary lifestyle, high-fat, high-calorie diet, stress, overeating, alcohol, and tobacco.
- Things to do: Maintain an appropriate weight. Maintain proper waist circumference. Regular exercise, a low-fat, low-calorie diet, and annual physical exam.
Who should be tested for diabetes regularly?
* For diagnosis of early stage diabetes without symptoms, it is recommended to check yearly blood glucose test for people who are:
- All adults aged 45 and over.
- Even if you are under 45 years old, if you are overweight or obese.
- People with high blood pressure or hyperlipidemia.
- A person who has diabetes among parents, siblings, and children.
- Anyone who has ever been diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
- People who have experienced cardiovascular disease.
- People who do not exercise normally.
Basic principles for diabetic patients?
- Keep hemoglobin A1C below 7.0%.
- Test for hemoglobin A1C at least twice a year (if well controlled) or four times a year (if not controlled well).
- Keep bad cholesterol (LDL) at least below 100.
- Keep blood pressure at least 140/90 (low risk group), or 130/80 (high risk group).
- Retinal eye examination is done once a year.
- Clean your feet every day and observe any abnormalities with the naked eye.
- At least once a year, have a foot examination by your doctor.
Glycemic Index (GI)?
- Glycemic Index is a relative ranking of carbohydrate in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates with a low GI value (55 or less) are more slowly digested, absorbed and metabolized and cause a lower and slower rise in blood glucose.
- Foods with a high glycemic index (over 70): white bread, white rice, white flour, potatoes, cereals, pineapple, mango, watermelon.
- Foods with a mild glycemic index (56-69): hamburgers, ice cream, sweet potatoes.
- Foods with a low glycemic index (less than 55): beans, peanuts, whole rye, barley, oats, lentils, quinoa, apples, bananas, tofu, carrots, fat-free milk.
Steven Koh, MD
Family Medicine
Edmonds Medical Clinic